Various medical conditions can cause scaly skin and can be treated using moisturizers, avoiding hot showers, and using ointments or creams. Persistent scaling should be discussed with a healthcare provider for further treatment options.
Causes Of Scaly Skin
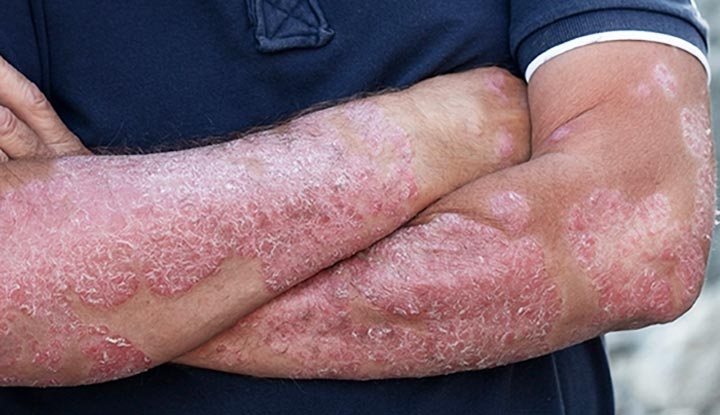
Various medical conditions, including psoriasis, contact dermatitis, eczema, and fungal skin infections, can cause scaly skin. Understanding the specific causes of scaly skin can help individuals identify the underlying issue and seek appropriate treatment options. Here are some common causes of scaly skin:
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing the formation of thick, scaly patches. These patches can appear anywhere on the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Psoriasis is characterized by accelerated skin cell turnover, which leads to a buildup of dead skin cells on the surface.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin directly contacts an irritant or allergen. This can be caused by exposure to certain chemicals, metals, fabrics, or even specific plants. The skin reacts by becoming red, itchy, and scaly. Identifying and avoiding the trigger is crucial to managing contact dermatitis.
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. This can lead to dryness and scaling. Various factors, including allergens, irritants, certain foods, stress, or climate changes can trigger eczema. Proper moisturization and avoiding triggers are essential in managing eczema.
Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections, such as ringworm or athlete’s foot, can cause scaly patches on the skin. Various fungi cause these infections, which are typically accompanied by itching, redness, and discomfort. Antifungal medications are often prescribed to treat these infections and alleviate the associated symptoms.
To effectively address scaly skin, understanding the underlying cause is crucial. Seeking medical advice from a healthcare provider can help determine the appropriate treatment options for individual cases.

Preventing Scaly Skin
To
Using Gentle, Fragrance-free Skin Care Products
Gentle, fragrance-free skin care products are essential for preventing scaly skin. Harsh chemicals and fragrances can irritate the skin and strip it of its natural moisture, leading to dryness and scaling. When choosing skin care products, look for those specifically formulated for sensitive skin and labeled as fragrance-free. These products are designed to be gentle on the skin and minimize the risk of irritation. Additionally, opt for products with moisturizing ingredients such as hyaluronic acid or ceramides to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
Avoiding Hot Showers And Baths
Hot showers and baths may feel soothing but can contribute to scaly skin. The hot water strips the skin of its natural oils, leaving it dry and prone to scaling. To prevent this, use lukewarm water instead of hot water when bathing. Limit your showers or baths to no more than 10–15 minutes to minimize the exposure of your skin to water. After bathing, pat your skin dry gently with a towel, leaving a little moisture on the skin. This helps to lock in hydration. Avoid rubbing or scrubbing the skin vigorously, which can further irritate and dry the skin.
Managing Stress
Stress can hurt your skin’s health, causing it to become dry and scaly. When stressed, your body releases cortisol, a hormone that disrupts the skin’s natural balance. To prevent scaly skin, it’s essential to manage your stress levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or yoga. Take time for yourself and prioritize self-care. Sleeping and maintaining a healthy diet can also help reduce stress and improve your skin’s overall health.
Minimizing Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure can dehydrate the skin and lead to dryness and scaling. Protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays is essential for preventing scaly skin. When outdoors, apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Wear protective clothing like hats and long sleeves to minimize direct sun exposure. Seek shade when the sun is at its strongest, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. By taking these preventive measures, you can help maintain your skin’s moisture balance and reduce the risk of scaly skin.
Treatment Options For Scaly Skin
When it comes to treating scaly skin, several options are available, depending on the severity of the condition. These treatment options aim to soothe the skin, reduce scaling, and restore its natural moisture balance. By understanding the different treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about the best method for their needs.
Moisturizers And Creams With Urea, Petrolatum, Or Lactic Acid
Moisturizers and creams that contain urea, petrolatum, or lactic acid are commonly used to alleviate the symptoms of scaly skin. These ingredients help to improve skin hydration and lock in moisture, preventing further dryness and scaling. Urea acts as a humectant, attracting and holding moisture in the skin. Petrolatum forms a protective barrier on the skin’s surface, preventing moisture loss. Lactic acid helps to exfoliate dead skin cells, promoting smoother and softer skin.
When choosing a moisturizer or cream, look for products specifically formulated for dry and scaly skin. These products should be fragrance-free and gentle to avoid irritation. Applying the moisturizer immediately after washing can maximize its effectiveness, as the skin absorbs the moisture better when damp. Regular and consistent use of these products can help restore the skin’s natural moisture balance and reduce scaling over time.
Prescription Medications
In more severe cases of scaly skin, prescription medications may be necessary. Dermatologists typically prescribe these medications and can offer targeted treatment for specific conditions that cause scaling, such as psoriasis or eczema. Prescription creams, ointments, or gels containing active ingredients like corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or retinoids can help to reduce inflammation, normalize skin cell growth, and alleviate symptoms like redness, itching, and scaling.
It is essential to follow healthcare professionals’ instructions when using prescription medications. These medications may have specific application guidelines and potential side effects. Regular check-ups and consultations with a dermatologist are also recommended to monitor the progress and adjust the treatment plan.
Topical Steroids
Topical steroids are another standard treatment option for scaly skin. These medications contain corticosteroids, which can help reduce swelling and relieve itching. Topical steroids come in various strengths and forms, such as creams, ointments, lotions, or gels. The specific steroid and application method will depend on the severity and location of the scaly skin.
It is essential to use topical steroids as directed by a healthcare professional. Overuse or misuse of these medications can lead to side effects such as skin thinning, discoloration, or rebound flare-ups. Dermatologists will typically prescribe the appropriate strength and duration of treatment based on the individual’s condition.
Systemic Treatments
In more severe cases of scaly skin that does not respond well to topical treatments, systemic treatments may be considered. These treatments are taken orally or through injection and work internally to target the underlying causes of the skin condition. Systemic therapies can include medications such as immunosuppressants, biologics, or oral retinoids.
Dermatologists or other healthcare professionals prescribe and monitor systemic therapies for scaly skin. They may be recommended for conditions like severe psoriasis or eczema that have not responded to different treatment approaches. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to ensuring the effectiveness and safety of these systemic treatments.

Frequently Asked Questions Of Scaly Skin – Causes, How To Prevent It, & Treatment Options
What Is The Fastest Way To Heal Scaly Skin?
To heal scaly skin fast, follow these tips: – Stop baths and showers from worsening dry skin. – Apply moisturizer immediately after washing. – Use an ointment or cream instead of a lotion. – Wear lip balm. – Use gentle, fragrance-free skin care products.
– Wear gloves to protect your skin. (Source: American Academy of Dermatology)
What Causes Scaly Skin And How Do You Treat It?
Conditions like psoriasis, contact dermatitis, eczema, and fungal infections can cause scaly skin. To treat it, moisturize immediately after washing, use ointments instead of lotions, wear lip balm, and use gentle, fragrance-free skin care products. Persistent scaling should be discussed with a healthcare provider for treatment options.
What Is The Best Medicine For Scaly Skin?
Topical treatments like salicylic acid solutions or creams can help with scaly skin. Moisturizers that prevent moisture loss are also recommended. Greasy ointments and cortisone-containing creams may provide relief. It’s essential to contact a healthcare provider for persistently scaling skin.
Can You Reverse Scaly Skin?
To reverse scaly skin, follow these tips: 1. Use moisturizer after washing. 2. Opt for ointments or creams rather than lotions. 3. Wear gloves to protect the skin. 4. Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products. 5. Consult a doctor for medicated products if needed.
Conclusion
When scaling skin, it is essential to address the underlying medical condition. This may include topical treatments such as salicylic acid solutions or creams, moisturizing the skin regularly with ointments or creams, and avoiding triggers that worsen dry skin. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment options for more severe cases.
Remember, maintaining proper skincare habits and seeking professional advice can help prevent and manage scaly skin effectively.
DIY hair oils are some of the most important ingredients to have in your beauty arsenal. They add shine, manage frizzy hair, and help improve your hair health.