Chemical burns are tissue damage caused by strong acids, drain cleaners, paint thinners, gasoline, and other substances. Symptoms include redness, irritation, burning, pain, numbness, blisters, black, dead skin, vision changes, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Treatment for a chemical burn involves first-aid measures and medical intervention. Various substances can cause chemical burns and significantly damage the skin and other tissues. Symptoms of a chemical burn may include redness, irritation, burning, pain, numbness, blister formation, black, dead skin, vision changes, coughing, and shortness of breath.
It is essential to seek proper treatment for a chemical burn to prevent further complications and promote healing.
Common Causes Of Chemical Burns
Chemical burns can occur when the skin or eyes come into contact with strong acids, bases, or other substances. Understanding the common causes of chemical burns can help prevent these accidents and mitigate their effects. Here are the three main categories of substances that can cause chemical burns:
Acids
Acids are one of the primary causes of chemical burns. They are corrosive substances that release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. Some common household acids that can cause burns include:
| Acids | Common Sources |
|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid | Battery acid, drain cleaners |
| Hydrochloric acid | Toilet bowl cleaners, swimming pool chemicals |
| Nitric acid | Fertilizers, metal cleaners |
When acids come into contact with the skin or eyes, they can cause severe damage, including tissue necrosis and chemical burns.
Bases
Bases, also known as alkalis, are another category of substances that can cause chemical burns. They are corrosive compounds that release hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. Some familiar sources of bases that can cause burns include:
| Bases | Common Sources |
|---|---|
| Sodium hydroxide | Drain cleaners, oven cleaners |
| Calcium hydroxide | Cement, plaster |
| Ammonia | Cleaning products, fertilizers |
Like acids, bases can cause significant damage to the skin and eyes upon contact, resulting in chemical burns.
Other Substances
Aside from acids and bases, various other substances can cause chemical burns. These substances may include:
- Potent oxidizing agents, such as hydrogen peroxide and chlorine
- Flammable chemicals, such as gasoline and lighter fluid
- Acidic substances, like paint thinner and industrial cleaners
Handling these substances carefully and following proper safety protocols to prevent chemical burns and other accidents is essential.
Understanding the common causes of chemical burns, including acids, bases, and other substances, is essential for promoting safety and preventing accidents. By being aware of the potential risks associated with these substances, individuals can take the necessary precautions to protect themselves and minimize the chances of chemical burn incidents.

Symptoms Of Chemical Burns
Symptoms of chemical burns include redness, irritation, burning, blisters or dead skin at the site of contact, vision changes if the chemical gets into the eyes, and coughing or shortness of breath. Strong acids, drain cleaners, paint thinners, gasoline, and other substances cause these burns.
Immediate treatment is necessary to prevent further damage.
Redness, Irritation, Or Burning At The Site Of Contact
One of the most common symptoms of a chemical burn is redness, irritation, or burning at the site of contact. When a harmful chemical comes into contact with your skin, it can cause immediate inflammation, leading to redness and irritation. This can be uncomfortable and may intensify if not appropriately treated.
Pain Or Numbness At The Site Of Contact
In addition to redness and irritation, a chemical burn can cause pain or numbness at the contact site. Depending on the severity of the burn, you may experience mild to severe pain. Numbness can occur due to the damage caused by the chemical on the nerve endings.
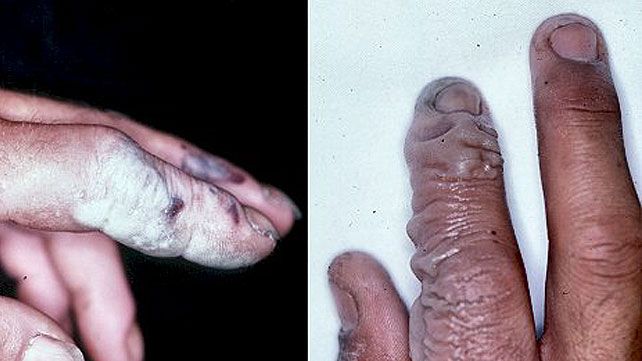
Formation Of Blisters Or Black Dead Skin At The Contact Site
Another symptom of a chemical burn is the formation of blisters or black, dead skin at the contact site. This occurs when the chemical damages the skin’s layers, leading to blisters filled with fluid. In more severe cases, the skin may turn black and become necrotic.
Vision Changes If The Chemical Gets Into Your Eyes
If a chemical comes into contact with your eyes, you may experience vision changes as a symptom of a chemical burn. This can include blurred vision, sensitivity to light, or even temporary vision loss. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if a chemical enters your eyes.
Cough Or Shortness Of Breath
Inhalation of certain chemicals can lead to respiratory symptoms such as coughing or shortness of breath. This can occur if the chemical enters your lungs, causing irritation and inflammation. If you experience these symptoms after exposure to a chemical, it is essential to seek medical assistance immediately.
Treatment For Chemical Burns
Chemical burns can cause redness, irritation, and blistering at the contact site. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, vision changes, coughing, and shortness of breath. Prompt treatment is crucial and may involve first-aid measures such as rinsing the affected area with water and seeking medical attention.
When it comes to treating chemical burns, prompt action is crucial in order to minimize damage and promote healing. The appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of the burn. Here are the different treatment options for chemical burns:
First Aid Measures
Immediate first-aid measures should be taken as soon as a chemical burn occurs. These steps can help minimize further damage and provide relief.
- Remove any clothing or jewelry that has come into contact with the chemical to prevent further exposure.
- Flush the affected area with cool, running water for at least 20 minutes. This will help remove the chemical and dilute its effects on the skin.
- Avoid ice or cold packs, as they can cause further tissue damage. Instead, use cool water to soothe the burn.
- Cover the burn with a sterile, non-stick dressing to protect it from infection.
- Seek immediate medical attention if the burn is extensive, covers sensitive areas such as the face or genitals, or if the chemical involved is known to be highly toxic.
Medical Treatment
Medical treatment may be necessary if the chemical burn is more severe or involves a more extensive body area. A healthcare professional will assess the burn and determine the appropriate course of action, which may include:
- Prescribing pain medications to manage discomfort.
- Administering tetanus shots if the burn is deep or contaminated.
- Apply topical antibiotics or ointments to prevent infection.
- Use dressings or bandages to promote healing and protect the affected area.
Specialized Treatment For Severe Burns
In severe chemical burns, specialized treatment may be required to optimize healing and cosmetic outcomes. This may involve:
- Referral to a burn specialist or plastic surgeon for further evaluation and management.
- Surgical interventions include debridement (removal of dead tissue) or skin grafting.
- Wound care techniques include specialized dressings, negative pressure therapy, or hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
- Physical and occupational therapy to restore functionality and minimize scarring.
- Psychological support to cope with the emotional impact of the burn injury.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations based on the specific circumstances of the chemical burn.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Chemical Burn: Common Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
What Are Symptoms Of A Chemical Burn?
Symptoms of a chemical burn include redness, irritation, or burning at the contact site; pain or numbness; blister formation; changes in vision if the chemical gets into the eyes; and coughing or shortness of breath. Seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
What Is The Most Likely Cause Of Chemical Burns?
Strong acids, drain cleaners, paint thinners, gasoline, and other substances cause chemical burns. You may not always immediately recognize a burn caused by a milder chemical.
What Is The Correct Treatment For A Chemical Burn?
The correct treatment for a chemical burn includes rinsing the affected area with cool running water for at least 20 minutes. Remove any clothing or jewelry that may have come into contact with the chemical. Seek medical attention for severe burns or those on sensitive areas like the face, hands, or genitals.
Apply a sterile dressing and take over-the-counter pain relievers if necessary.
What Is The Most Common Treatment For Burns?
The most common treatment for burns is to cool the burn by running cool water for about 20 minutes. Do not use ice or icy water. Cover the burn with a clean, dry dressing. Seek medical attention for more extensive or more severe burns.
Conclusion
Chemical burns can be a painful and dangerous experience, and it’s essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available. Symptoms of a chemical burn include redness, pain, blisters, and vision changes if the chemical gets into the eyes.
Prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial to minimize damage and prevent complications. Remember to seek medical attention if you experience a chemical burn, as healthcare professionals can provide the necessary care and guidance for a safe recovery. Stay informed and take precautions to avoid chemical burns whenever possible.
DIY hair oils are some of the most important ingredients to have in your beauty arsenal. They add shine, manage frizzy hair, and help improve your hair health.