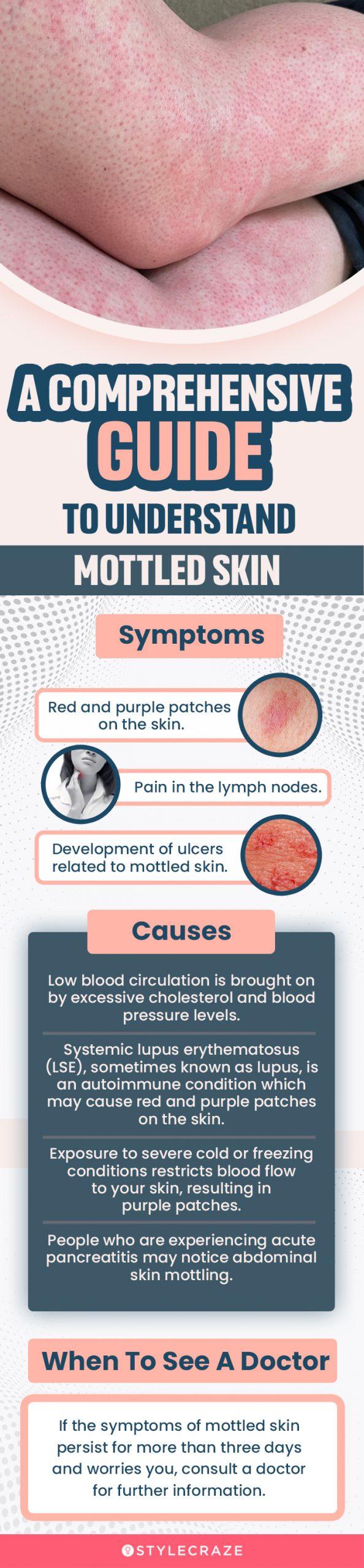
Mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is characterized by a bluish-red, lace-like pattern under the skin. It can be caused by cold exposure or chronic medical conditions.
Treatment is typically not required, and skin warming can reduce symptoms. However, if the mottled skin does not go away with warming or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms or painful lumps, it is essential to see a healthcare provider.
Mottled skin can be associated with underlying disorders such as thyroid disease and acute pancreatitis. If an underlying disorder is present, there may be additional symptoms. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of mottled skin can help individuals better manage and address this condition.

Causes Of Mottled Skin
Mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is characterized by a bluish-red, lace-like pattern under the skin. This discoloration occurs when deoxygenated blood pools beneath the skin’s surface. While mottled skin is typically harmless and temporary, it can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions or environmental factors. Understanding the causes of blotchy skin can help individuals identify the root of their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
Lack Of Blood Circulation
A lack of blood circulation is one of the primary causes of mottled skin. When blood circulation is compromised, particularly in the extremities, it can lead to discoloration and mottling. Conditions such as peripheral artery disease, blood clots, and arterial blockages can restrict blood flow, causing mottled skin. Poor circulation can also result from lifestyle factors, such as prolonged sitting or standing, obesity, and smoking.
Cold Exposure
Cold exposure is another common cause of mottled skin. When the body is exposed to freezing temperatures, the blood vessels in the skin constrict to conserve heat. This constriction can cause mottling and a bluish discoloration due to reduced blood flow to the skin. Cold-induced mottled skin is often temporary and resolves once the body warms up. However, prolonged exposure to extreme cold or cold-related disorders like frostbite can result in persistently blotchy skin.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Mottled skin can also be a symptom of underlying medical conditions. Various systemic diseases and disorders can cause blotchy skin due to impaired blood flow, inflammation, or vascular abnormalities. Some of the medical conditions associated with blotchy skin include:
- Autoimmune diseases include systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma, and Sjögren’s disease.
- Dermatological conditions like dermatomyositis and Still’s disease.
- Rheumatoid arthritis may indicate rheumatoid vasculitis if mottled skin is present.
- Other vascular disorders, like peripheral artery disease and blood clotting disorders,.
If an individual notices persistent mottled skin or experiences other concerning symptoms alongside it, it is essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms Of Mottled Skin
Mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is characterized by a bluish-red, lace-like pattern beneath the skin. Various factors, such as cold exposure and chronic medical conditions, can cause it. Although usually harmless, it is essential to seek medical advice if the discoloration persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Blotchy Appearance
Mottled skin is characterized by its blotchy appearance, which can be described as a patchy or uneven distribution of color on the skin’s surface. The affected areas may appear mottled, meaning they have a marbled or veined pattern. This blotchy appearance is often more visible on areas of the body with thinner skin, such as the hands, fingers, feet, and legs.
Red Or Purple Spots
One of the critical symptoms of mottled skin is the presence of red or purple spots on the affected areas. These spots can vary in size and shape and may be clustered or scattered across the skin. They are caused by the pooling of deoxygenated blood beneath the skin’s surface. These red or purple spots can make the skin discolored and uneven.
Irregular Skin Color
Another symptom of mottled skin is an irregular skin color. The affected areas may have a bluish, reddish, or purplish hue, contrasting with the surrounding healthy skin. This rare skin color results from compromised blood flow to the affected areas. The skin may also appear pale or have a grayish tint due to poor circulation.
In conclusion, the symptoms of mottled skin include a blotchy appearance, red or purple spots, and irregular skin color. These symptoms can vary in severity and may be more noticeable in some body regions. If you notice these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Mottled Skin
Mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is characterized by a bluish-red, lace-like pattern under the skin. Various factors, including cold exposure and chronic medical conditions, can cause it. Although typically harmless, if the mottled skin persists even after warming or other concerning symptoms accompany it, it is advised to consult a healthcare provider.
If you or someone you know has experienced mottled skin, it is essential to understand the diagnosis and treatment options available. Blotchy skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is characterized by a bluish-red or lace-like pattern underneath the skin’s surface. It can occur due to various factors, including cold exposure and chronic medical conditions. Medical professionals typically perform a combination of medical examinations, history analysis, and laboratory tests to diagnose and treat mottled skin properly.
Medical Examination And History
The healthcare provider will observe the affected areas during a medical examination for mottled skin. They may ask questions about the appearance, duration, and accompanying symptoms to gather a comprehensive medical history. It is essential to provide accurate information related to family history, current medications, and any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to the development of mottled skin.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests may be conducted to investigate the underlying causes of mottled skin further. This can include blood tests to check for abnormalities in blood cell count, coagulation factors, and autoimmune markers. Additionally, imaging tests such as ultrasound or angiography may be recommended to evaluate the condition of blood vessels and circulation.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for mottled skin generally depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. No specific treatment may be needed in cases where blotchy skin is a benign and temporary phenomenon. However, if blotchy skin is associated with an underlying medical condition or results in discomfort, the healthcare provider may recommend the following treatment approaches:
- Managing the underlying condition: If mottled skin is a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as autoimmune diseases or vascular disorders, treating and managing the primary condition may help alleviate the symptoms.
- Addressing temperature sensitivity: As cold exposure can worsen mottled skin, individuals may be advised to keep the affected areas warm by wearing appropriate clothing, heating pads, or warm compresses.
- Improving circulation: Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or massage, may help improve blood circulation and reduce the appearance of mottled skin.
- Medication: In some instances, medications such as vasodilators or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and promote better blood flow.
- Consulting a specialist: Depending on the severity and underlying cause of mottled skin, a referral to a dermatologist, rheumatologist, or vascular specialist may be recommended for further evaluation and specialized treatment options.
It is important to remember that qualified healthcare professionals should diagnose and treat mottled skin. If you or someone you know is experiencing blotchy skin, it is advisable to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Frequently Asked Questions Of Mottled Skin: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, And Treatment
How Do You Treat Mottled Skin?
Mottled skin can be treated by warming the skin to help the blood vessels open up again. It is more common in children and young women and is usually harmless, not requiring treatment. If the mottled skin doesn’t go away or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is best to see a healthcare provider.
When Is Mottled Skin A Concern?
Mottled skin is a concern if it doesn’t go away with warming if other concerning symptoms accompany it, or if painful lumps develop. It can indicate an underlying disorder, such as autoimmune diseases or poor circulation.
See a healthcare provider for evaluation.
What Autoimmune Disease Causes Livedo Reticularis?
Livedo reticularis is most commonly associated with autoimmune diseases like SLE, systemic sclerosis, Sjögren’s disease, dermatomyositis, and Still’s disease. It can also be a sign of rheumatoid vasculitis.
What Does It Mean When A Patient Is Mottled?
Mottled skin refers to the appearance of red or purple spots on the skin, often seen at the end of life. It is caused by poor circulation when the heart can no longer pump blood effectively. Mottling is a harmless condition that does not require treatment, but warming the skin can help reduce symptoms.
Conclusion
Mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis, is a common condition affecting adults and children. While it is usually harmless and does not require treatment, it is essential to seek medical attention if the discolored skin does not go away with warming or if other concerning symptoms develop.
Mottled skin can indicate an underlying disorder, so it is essential to address any accompanying symptoms. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for mottled skin, individuals can better manage their condition and seek appropriate medical care.
DIY hair oils are some of the most important ingredients to have in your beauty arsenal. They add shine, manage frizzy hair, and help improve your hair health.